QuaSi II
Back to project overviewProject description
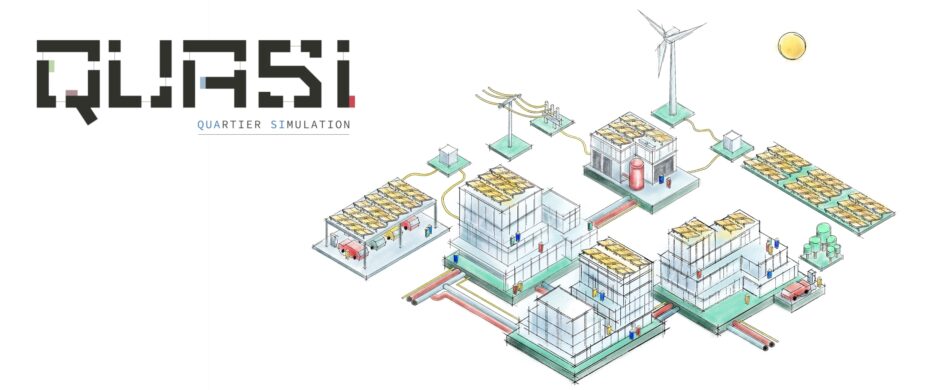
As part of the Klimaquartier Neue Weststadt Esslingen project, the simulation tool "QuaSi"(Quartier-Simulation) was developed for planning and evaluating the energy supply of urban districts. It is based on a dynamic energy simulation and can map different supply concepts for urban districts. The "GenSim" tool for generic thermal building simulation was also created to determine the energy requirements of the buildings in an urban district. Both tools were used to design and plan the innovative energy concept for the "Klimaquartier Neue Weststadt Esslingen" and have also been successfully applied in other research and planning projects.
In April 2022, the 3-year joint project QuaSi_II started with Digital Building Industries AG (DBI) as a joint partner. In the project, the existing simulation tools are being further developed and integrated into DBI's web-based BIM tool Building Configurator. In addition to the expansion of the implemented building and plant models, the functionality of the simulation tools will also be greatly expanded as part of the new research project, including a life cycle cost analysis, an optimization process and a sensitivity analysis. In order to examine and evaluate the quality of the results, automated test environments and validations will be carried out against simulation and measurement results. The calculation kernels and tools programmed by the siz are published as open-source software and are to be further developed in a participatory, application-oriented manner.
Under the QuaSi Software umbrella, the QuaSi_II project will essentially (further) develop three simulation tools and integrate them into the commercial BIM tool Building Configurator:
- GenSim for generic thermal building simulation based on EnergyPlusTM
- Sodele for the simulation of yields from PV systems based on the Python library "pvlib"
- ReSiE as a new calculation kernel developed from scratch in the Julia programming language for simulating the energy supply of urban districts. This new calculation kernel replaces the previous simulation tool QuaSi, which was developed in the aforementioned Klimaquartier Neue Weststadt Esslingen research project.
All three components are or will be published on the GitHub project page. In addition, detailed online documentation is being created for the use of and collaboration on the published tools. This includes technical basics and mathematical descriptions of the implemented models.
In line with the Energiewendebauen research initiative, the overarching aim of the research project is to research and optimize the complex interaction between building and neighbourhood-related technologies and the residents. The overarching goal of this optimization is to achieve the most climate-neutral building standard possible in new and existing buildings. The focus here is on measures such as decentralized generation of renewable energies, increasing efficiency through sector coupling (primarily electricity, heat, industry and mobility) and energy-efficient integration into the overarching (increasingly renewable) electricity infrastructure. The practical implementation of these measures in the form of a holistic energy supply concept requires a high degree of intelligent networking between the energy systems and the residents as well as the use of appropriate operating strategies.
Simulation models are an indispensable tool for planning and developing supply concepts that meet these requirements in practice. The complex interrelationships and energy flows, as well as the necessary operating strategies, cannot be mapped effectively using conventional static calculation approaches. This is mainly due to the high degree of networking and interaction through sector coupling and the volatile availability of renewable energies from wind power and solar energy.
The main aim of the research project is therefore to provide comprehensive simulation software for planning and evaluating possible energy supply concepts and operating strategies for urban districts for use in early planning phases. The target group includes specialists in the field of planning as well as experts in engineering and science.
- Digital Building Industries (DBI)
AB 1 Model description and re-implementation
AB 2 User interface and integration in building configurator (GKf)
AB 3 Test environment and validation
AB 4 Extension of the model and functionality
AB 5 Publication and documentation